What Is For Loop In Python?
A for loop in Python is used to repeat a set of actions for each item in a sequence, like a list, string, or range of numbers. It helps you go through each element and do something with it, such as printing or performing a calculation. It’s commonly used when you know in advance how many times you want to execute a statement or a block of statements.
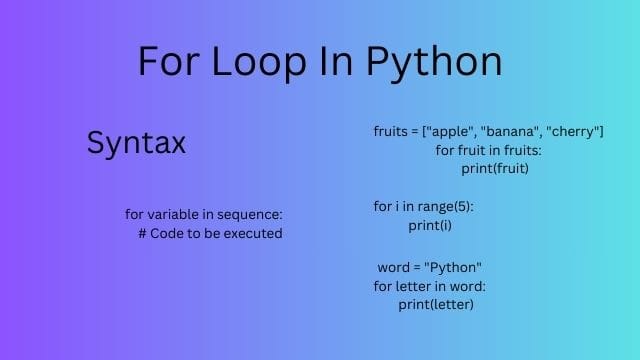
Syntax of For Loop In Python:
for variable in sequence:
—-# Code to be executed
- variable: This is a placeholder that takes the value of each item in the sequence during each iteration.
- sequence: This can be a list, range, string, or any other iterable.
Indentation in Loop
Indentation in Python means adding spaces at the start of a line to define blocks of code. It is required to show which lines belong together, such as in loops or functions.
for i in range(5):
—-print(I) # This line is indented, so it’s part of the loop block
print(“Done”) # This line is not indented, so it’s outside the loop
Example 1: For Loop IteratingThrough a String:
word = “Python”
for letter in word:
—-print(letter)
Output:
P
y
t
h
o
n
In this example, each character in the string word is printed one by one.
Example 2: For Loop Iterating Through a List
fruits = [“apple”, “banana”, “cherry”]
for fruit in fruits:
—-print(fruit)
Output:
apple
banana
cherry
In this example, the for loop goes through each item in the fruits list and prints it.
In the above example, we have created a list named fruits. As the list has 3 elements, the loop iterates 3 times.
The value of fruit is
- apple in the first iteration.
- banana in the second iteration.
- cherry in the third iteration.
Example 3: For Loop In Python Using range()
In Python, the range () function returns a sequence of numbers. For example,
count = range(4)
Here, range() returns a sequence of 0,1,2,3. The sequence starts at 0.
Since the range() function returns a sequence of numbers, we can iterate over it using a for loop.
Example:
for i in range(5):
—-print(i)
Output:
0
1
2
3
4
The range(5) function generates numbers from 0 to 4, and the loop prints each number.
Example 4: Using for Loop with if Conditional statement
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
for num in numbers:
if num % 2 == 0:
—-print(f”{num} is even”)
Output:
2 is even
4 is even
In this example, the for loop iterates through the numbers list and check if each number is even.
The for loop in Python is a powerful tool for iterating over sequences and performing repetitive tasks in Python.
Nested For Loop In Python
A nested for loop in Python is a for loop inside another for loop. It is used to perform repeated actions at multiple levels, like iterating over rows and columns in a grid.
Example 1:
for i in range(3): # Outer loop
—-for j in range(2): # Inner loop
——–print(f”i: {i}, j: {j}”)
Output 1:
i: 0, j: 0
i: 0, j: 1
i: 1, j: 0
i: 1, j: 1
i: 2, j: 0
i: 2, j: 1
In this example, the outer loop runs 3 times, and for each iteration of the outer loop(0,1,2), the inner loop runs 2(0,1) times.
Example 2:
for row in range(1, 4): # Outer loop for rows
—-for col in range(1, 3): # Inner loop for columns
——–print(f”Row: {row}, Column: {col}”)
Output 2:
Row: 1, Column: 1
Row: 1, Column: 2
Row: 2, Column: 1
Row: 2, Column: 2
Row: 3, Column: 1
Row: 3, Column: 2
In this example, the outer loop goes through each row, and for each row, the inner loop goes through each column.
Example that uses break, continue, and pass in a for loop:
# Example with break
for num in range(5):
—-if num == 3:
——–break # Stop the loop when num is 3
—-print(num)
print(“—–“)
# Example with continue
for num in range(5):
—-if num == 3:
——–continue # Skip the rest of the code when num is 3
—-print(num)
print(“—–“)
# Example with pass
for num in range(5):
—-if num == 3:
——–pass # Do nothing when num is 3, just skip to the next iteration
—-print(num)
Output:
0
1
2
—–
0
1
2
4
—–
0
1
2
3
4