Welcome to Python Programming
Python is one of the most popular programming languages today. It is known for its simplicity and readability, making it an excellent choice for beginners and experienced programmers alike. In this blog post, we’ll introduce you to Python programming and show you why it’s a great language to learn.
Why Learn Python?
Python is a versatile language used in various fields, including web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and more. Here are a few reasons why you should learn Python:
Easy to Read and Write
Python has a simple syntax that closely resembles English, making it easy to read and write. This simplicity allows you to focus on learning programming concepts rather than struggling with complex syntax.
Versatile and Powerful
Python can be used for many different types of projects. Whether you’re interested in building websites, analyzing data, or creating games, Python has the tools and libraries to help you succeed.
Large Community and Support
Python has a large and active community of developers. This means that there are plenty of resources available, including tutorials, forums, and documentation, to help you learn and troubleshoot issues.
Setting Up Python on Your Computer
Before you can start programming in Python, you need to install it on your computer. Follow these simple steps to set up Python on Windows 10.
Step 1: Download Python
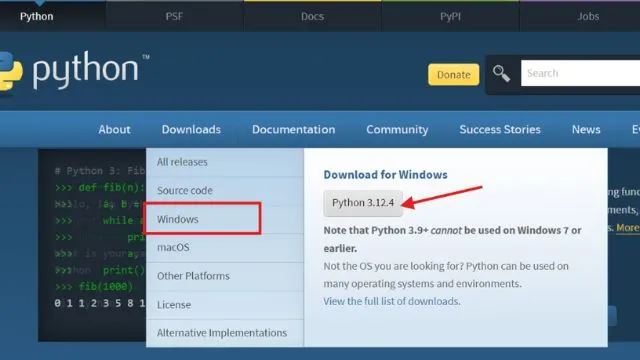
- Go to the official Python website: python.org.
- Click on the “Downloads” tab and choose the latest version of Python for Windows.
Step 2: Install Python
- Open the downloaded installer.
- Make sure to check the box that says “Add Python to PATH.”
- Click on “Install Now” and follow the prompts.
Step 3: Verify the Installation
- Open Command Prompt.
- Type
python --versionand press Enter. - You should see the installed Python version displayed.
Writing Your First Python Program
Now that you have Python installed, let’s write your first Python program. We’ll start with a simple “Hello, World!” program.
Step 1: Open a Text Editor
You can use any text editor to write Python code. For beginners, we recommend using IDLE, which comes with the Python installation.
Step 2: Write the Code
Type the following code into your text editor:
print("Hello, World!")Step 3: Run the Program
- Save the file with a
.pyextension, for example,hello.py. - Open Command Prompt and navigate to the folder where you saved the file.
- Type
python hello.pyand press Enter. - You should see the message “Hello, World!” printed on the screen.
Understanding the Code
Let’s break down the code you just wrote.
print(): This is a function that outputs the text inside the parentheses to the screen."Hello, World!": This is a string, a sequence of characters enclosed in quotes.
Basic Python Concepts
Before diving deeper into Python programming, it’s essential to understand some basic concepts.
Variables
Variables are used to store data that you can use and manipulate in your programs. Here’s an example:
message = "Hello, Python!"
print(message)
In this code, message is a variable that holds the string “Hello, Python!”.
Creating Variables
In Python, you don’t need to declare a variable explicitly. Variable names are created the moment you first assign a value to them.
x = 5
name = “Deepa”
Variable Naming Rules
- Variable names must start with a letter (a-z, A-Z) or an underscore (_).
- The name can contain letters, numbers (0-9), and underscores.
- Variable names are case-sensitive (
nameandNameare different variables).
Assigning Values to Variables
You can assign any type of value to a variable, and the same variable can hold different types of values over its lifetime.
age = 25 # Integer
height = 5.9 # Float
name = “Alice” # String
is_student = True # Boolean
Multiple Assignments
You can assign multiple variables in a single line.
a, b, c = 1, 2, 3
x = y = z = “same value”
Type of a Variable
Python is dynamically typed, meaning you don’t need to declare the type of a variable. The type is determined at runtime.
number = 10
print(type(number)) # Output: <class ‘int’>
text = “Hello”
print(type(text)) # Output: <class ‘str’>
Best Practices
- Use descriptive names for variables to make the code more readable.
- Follow the convention of using lowercase letters and underscores for variable names (e.g.,
user_name,total_amount).
Example
Here’s a simple example demonstrating variable usage in Python:
# Assign values to variables
name = “Deepa”
age = 30
is_teacher = True
# Print variable values
print(“Name:”, name)
print(“Age:”, age)
print(“Is Teacher:”, is_teacher)
Summary
- Variables are used to store data.
- No explicit declaration is required.
- Naming rules include starting with a letter or underscore and being case-sensitive.
- Dynamic typing allows variables to change types.
Understanding these basics helps in writing clear and efficient Python code.
Data Types
Python supports various data types, including integers, floats, strings, and lists. Here are some examples:
number = 10 # Integer
pi = 3.14 # Float
greeting = "Hi!" # String
numbers = [1, 2, 3] # List
Control Structures
Control structures allow you to control the flow of your program. The most common ones are if statements and loops.
If Statements
age = 18
if age >= 18:
print("You are an adult.")
else:
print("You are a minor.")
Loops
for i in range(5):
print(i)
This loop will print the numbers 0 to 4.
Read:
Python Programming for Beginners:
Conclusion:
Welcome to the exciting world of Python programming! With its simplicity and versatility, Python is an excellent language for both beginners and experienced programmers. We hope this introduction has given you a good starting point. Stay tuned for more in-depth tutorials and guides on Python programming. Happy coding!
By following this guide, you’re well on your way to becoming proficient in Python. Don’t hesitate to explore more and practice regularly. Remember, the key to learning programming is consistency and curiosity.
Thank you for taking the time to read our blog on Python programming! We hope you found the information helpful and that you’re excited to start or continue your Python journey. Your support means a lot to us. If you have any questions or need further clarification on any topic, please leave a comment below. We’re here to help and look forward to hearing from you!
Are there specific Python topics or tutorials you would like to see in future blog posts?